- Home
- Energy Storage & Conversion Technologies
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery.
Battery and Inverters Technologies
- To develop superior and best in class technologies for Inverters and converters and other storage devices.
- To develop fast charging, high storage and longer lasting battery technologies by developing novel anode and cathode materials and study effect of material type, size, microscale processes, material characteristics, cell and pack design, and charging strategy optimisation etc.
- To develop standardised protocols for battery life testing and lifetime prediction.
- Thorough understanding of ageing and degradation through combination of tests, models and prediction focused in one system.
- To have the cost reductions via better understanding of ageing – optimisation of battery size and specifications, materials resistant to ageing etc.
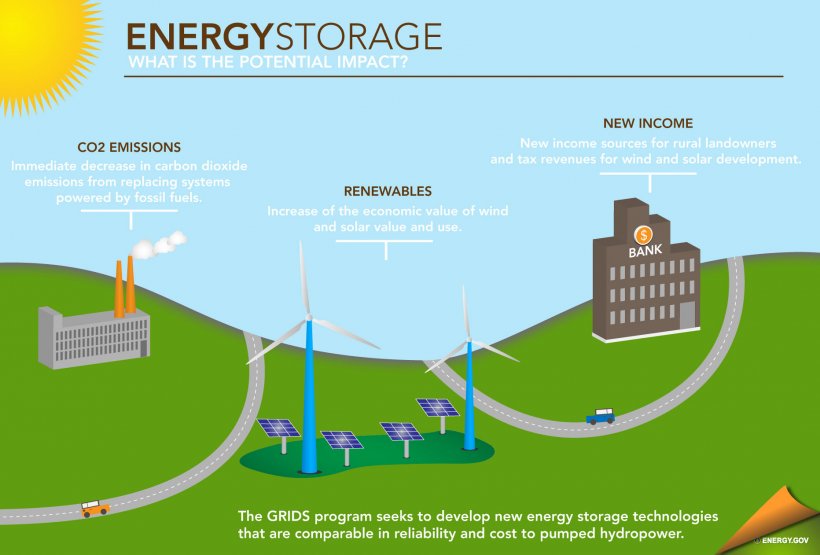
Energy storage has many benefits. It is particularly important for the development and integration of renewable energy technologies. Some renewable energy sources have intermittent generation profiles. For solar and wind energy, for example, this means that electricity is only produced when the sun is shining or when the wind is blowing. Such a situation creates supply and demand discrepancies because consumers may still require electricity when renewable sources are not producing.
Energy storage is also commonly used to smooth minor fluctuations in energy output for small and large electricity generation sources. Furthermore, energy storage provides increased reliability and strengthens system resilience at large and small substation levels. Energy storage is commonly used in transportation devices, like electric vehicles, trains, and bikes. Energy storage systems have traditionally been very expensive and not economically viable on a large scale. However, significant improvements in energy storage technologies have reduced costs and improved technology applications, and continue to do so today.